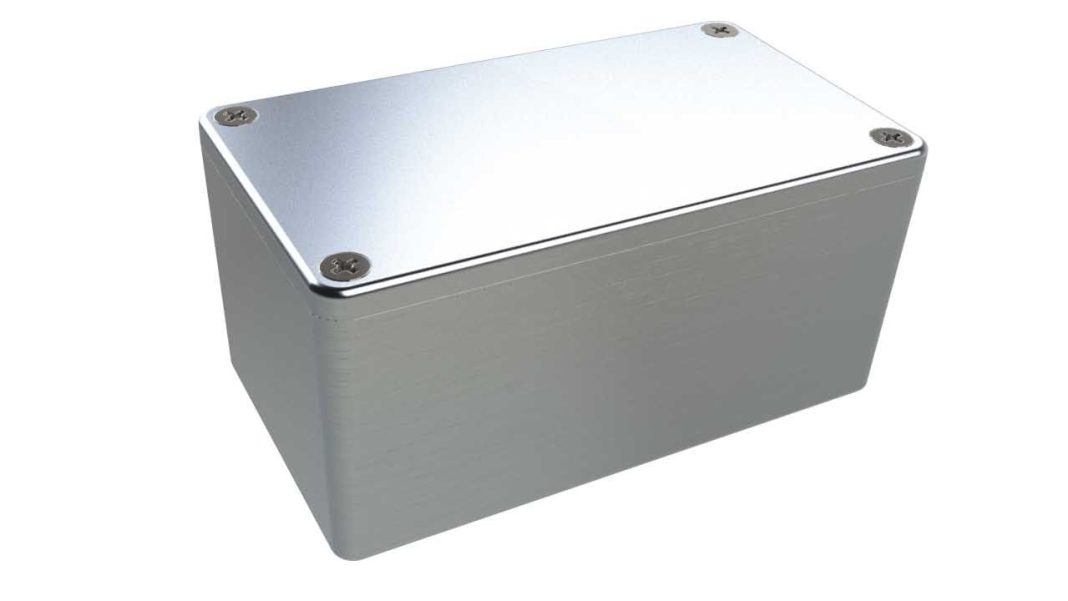
In the world of electronics, safeguarding sensitive components is paramount. Electronic metal housings are robust, versatile solutions that provide protection against environmental hazards, mechanical stress, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern applications, these housings ensure the longevity and reliability of critical electronic devices.
This guide explores the types, materials, benefits, and key considerations when choosing electronic metal housings for your specific needs.
What Are Electronic Metal Housings?
Electronic metal housings are protective enclosures made primarily from metal alloys. They encase electronic components such as circuit boards, power supplies, and sensors, shielding them from external damage and enhancing operational performance. These housings are widely used across industries like automotive, telecommunications, aerospace, and industrial automation.
Types of Electronic Metal Housings
Electronic metal housings come in various designs tailored to specific applications. Common types include:
1. Wall-Mounted Housings
- Ideal for space-saving installations.
- Commonly used in control panels and industrial settings.
2. Rack-Mount Enclosures
- Designed to fit into standard racks for telecommunications and data centers.
- Offer easy access for upgrades and maintenance.
3. Portable Cases
- Lightweight and rugged designs for mobile applications.
- Often feature shock-absorbing properties for added protection.
4. Sealed Enclosures
- Provide high ingress protection (IP ratings) to prevent water, dust, and other contaminants from entering.
- Essential for outdoor and hazardous environments.
5. Custom Enclosures
- Tailored designs for specific electronic systems.
- Allow integration of unique features, such as cutouts for ports and displays.
Materials Used in Electronic Metal Housings
The choice of material affects the enclosure’s durability, weight, and protective capabilities. Common materials include:
1. Aluminum
- Lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant.
- Excellent for applications requiring heat dissipation.
2. Steel
- Provides superior strength and rigidity.
- Often used in environments where impact resistance is critical.
3. Stainless Steel
- Highly resistant to rust and corrosion.
- Ideal for harsh or marine environments.
4. Copper Alloys
- Offer superior EMI shielding capabilities.
- Commonly used in telecommunications and sensitive electronic devices.
Benefits of Electronic Metal Housings
1. Enhanced Protection
- Shields components from physical damage, environmental hazards, and electrical interference.
2. Improved Heat Management
- Metals like aluminum and steel help dissipate heat, reducing the risk of overheating.
3. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding
- Metal enclosures block EMI and radio frequency interference (RFI), ensuring optimal performance in electronic systems.
4. Durability and Longevity
- Metal housings are highly resistant to wear and tear, extending the lifespan of electronic devices.
5. Aesthetic and Functional Design
- Metal enclosures can be finished with coatings or paint, enhancing appearance while adding corrosion resistance.
Key Considerations for Choosing Electronic Metal Housings
When selecting a metal housing, consider the following:
1. Environmental Conditions
- Determine the exposure to moisture, dust, temperature extremes, or corrosive substances. Opt for sealed enclosures or stainless steel for challenging conditions.
2. Size and Customization
- Ensure the housing accommodates your components with room for ventilation and future upgrades. Custom enclosures provide flexibility in design.
3. EMI/RFI Shielding Requirements
- If electromagnetic interference is a concern, prioritize materials with high shielding effectiveness.
4. Thermal Management
- For systems that generate heat, consider enclosures with ventilation or integrated cooling solutions.
5. Ease of Access
- Look for designs with removable panels or doors for convenient maintenance and repairs.
6. Compliance with Standards
- Ensure the housing meets relevant industry standards, such as IP ratings for ingress protection or NEMA ratings for durability.
Applications of Electronic Metal Housings
Electronic metal housings are used in diverse industries, including:
- Telecommunications: Protecting servers, routers, and signal processing equipment.
- Automotive: Housing for control modules, sensors, and navigation systems.
- Aerospace: Shielding avionics and other sensitive components.
- Industrial Automation: Safeguarding PLCs, motor controllers, and instrumentation.
- Consumer Electronics: Encasing high-end audio equipment and gaming systems.
The Future of Electronic Metal Housings
As technology advances, electronic metal housings are evolving to integrate smart features like IoT connectivity, real-time monitoring, and enhanced thermal solutions. These innovations cater to the increasing demand for compact, efficient, and reliable electronic systems in various industries.
Conclusion
Electronic metal housings are essential for protecting sensitive components in diverse applications. Their durability, heat management capabilities, and EMI shielding make them a top choice for modern electronics. By selecting the right housing for your specific needs, you can ensure the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electronic systems, even in the most challenging environments.