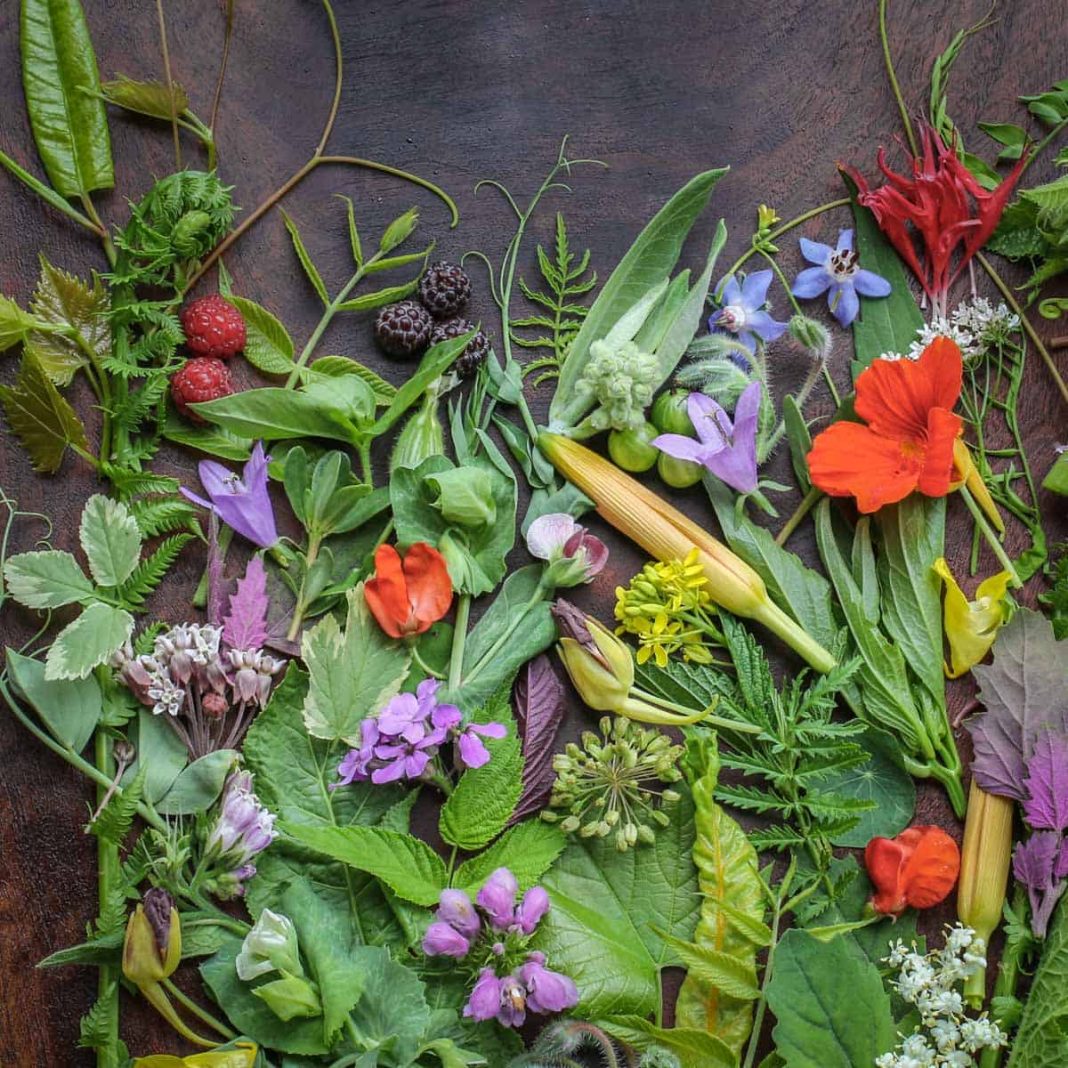
Survival foraging is an essential skill for anyone who spends time in the great outdoors. It not only enhances your connection to nature but also provides a source of nutrition when conventional food supplies are unavailable. Understanding how to identify and use wild food is crucial for survival situations, and being knowledgeable about wild food foraging can significantly increase your chances of thriving in the wilderness.
In this guide, we will explore the fundamentals of survival foraging, focusing on how to recognize edible plants and safely prepare them for consumption. It’s vital to have a keen eye for identifying wild edibles, as many plants can appear similar, and some are toxic. Learning to distinguish between safe and harmful options is essential. Start by familiarizing yourself with local edible plants and mushrooms before heading into the wild.
Identifying Wild Foods
- Research Local Flora: Before foraging, take time to learn about the edible plants in your area. Field guides, online resources, and local foraging groups can be invaluable in providing information on wild food sources.
- Know the Key Characteristics: When identifying wild foods, pay attention to specific traits such as leaf shape, flower color, and growth patterns. For example, dandelion leaves are jagged and grow low to the ground, while clover has three leaflets that form a triangular shape.
- Use the “Universal Edibility Test”: If you’re unsure whether a plant is safe to eat, you can perform the universal edibility test. Start by selecting a small piece of the plant, then crush it and apply it to your wrist for a few hours to check for allergic reactions. If there’s no adverse reaction, chew a small piece and wait 24 hours before swallowing to monitor for any negative effects.
Harvesting and Using Wild Foods
- Sustainable Harvesting: Always practice responsible foraging by only taking what you need and leaving plenty for wildlife and future growth. Use clean tools to harvest, and avoid overharvesting any single area.
- Preparation and Cooking: Many wild foods can be eaten raw, but some may require cooking to improve taste or reduce toxicity. For instance, certain mushrooms should be cooked thoroughly to eliminate harmful compounds. Make sure to wash all gathered food properly before consuming.
- Creating a Foraging Kit: Having a small kit with essential tools such as a pocket knife, foraging bag, and a field guide can make the foraging experience more efficient and enjoyable.
Conclusion
Survival foraging equips you with the skills necessary to identify and utilize wild food in nature. By embracing the principles of wild food foraging, you’ll enhance your outdoor adventures while ensuring that you are prepared for any situation that may arise. Always prioritize safety, sustainability, and knowledge as you explore the vast array of edible plants and mushrooms available in your local environment.