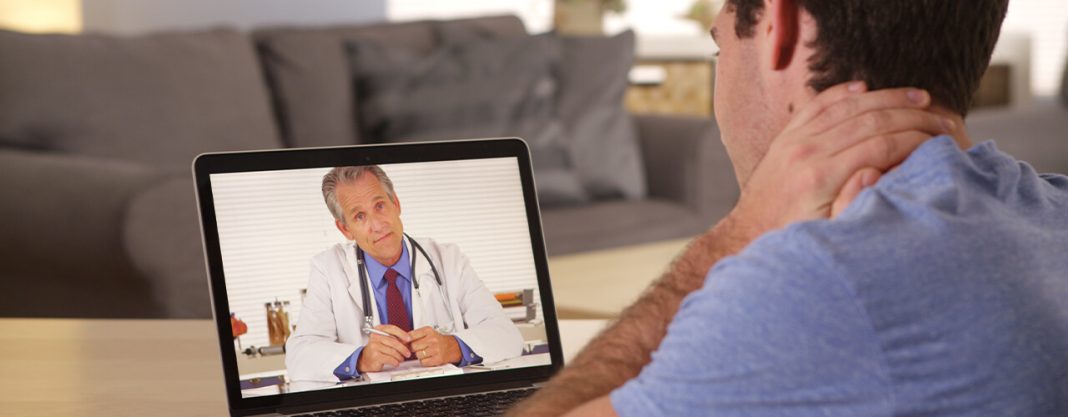
Introduction: Telehealth has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare, offering unprecedented convenience and accessibility to individuals across Connecticut. In this article, we explore the landscape of telehealth in Connecticut, examining its benefits, applications, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding Telehealth: Telehealth, also known as telemedicine, refers to the delivery of healthcare services remotely using telecommunications technology. Through video conferencing, phone calls, secure messaging, and other digital platforms, telehealth enables healthcare providers to connect with patients, diagnose conditions, prescribe treatments, and offer medical advice without the need for in-person visits.
The Rise of Telehealth in Connecticut: In recent years, telehealth has experienced rapid growth and adoption in Connecticut, driven by technological advancements, changing healthcare needs, and the COVID-19 pandemic. With its vast rural areas, transportation challenges, and diverse population, Connecticut stands to benefit significantly from the expansion of telehealth services.
Benefits of Telehealth in Connecticut: Telehealth offers numerous advantages for patients, healthcare providers, and the healthcare system as a whole in Connecticut:
- Improved Access to Care: Telehealth eliminates geographical barriers, allowing individuals in remote or underserved areas to access healthcare services without the need for travel.
- Convenience and Flexibility: Patients can receive medical care from the comfort of their homes, saving time and reducing the burden of scheduling conflicts and transportation issues.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Telehealth consultations often cost less than in-person visits, resulting in savings for both patients and healthcare providers.
- Continuity of Care: Telehealth facilitates ongoing monitoring and follow-up care, enabling healthcare providers to maintain regular contact with patients and manage chronic conditions effectively.
- Reduced Risk of Infection: During public health emergencies such as the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth minimizes the risk of exposure to infectious diseases by limiting in-person contact.
Applications of Telehealth in Connecticut: Telehealth has a wide range of applications across various medical specialties and healthcare settings in Connecticut:
- Primary Care: Telehealth consultations allow patients to consult with primary care physicians for routine check-ups, minor illnesses, and medication management.
- Specialty Care: Telehealth enables patients to access specialized medical services, such as dermatology, psychiatry, and cardiology, without the need for referrals or lengthy wait times.
- Mental Health Services: Telehealth expands access to mental health counseling, therapy, and psychiatric services, particularly in areas with a shortage of mental health providers.
- Chronic Disease Management: Telehealth platforms support remote monitoring and management of chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
- Urgent Care: Telehealth services offer timely medical advice and treatment for non-emergency health issues, reducing unnecessary emergency room visits and alleviating strain on hospital resources.
Challenges and Considerations: While telehealth offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges and considerations in Connecticut:
- Digital Divide: Disparities in internet access, digital literacy, and access to technology may limit the adoption of telehealth among underserved populations, exacerbating existing healthcare inequities.
- Reimbursement Policies: Uncertainty surrounding reimbursement policies and coverage for telehealth services may deter healthcare providers from offering telehealth options or limit patient access to affordable care.
- Privacy and Security: Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data transmitted through telehealth platforms is essential to maintaining patient trust and compliance with healthcare regulations.
- Regulatory and Licensure Issues: State licensure requirements, credentialing processes, and regulatory frameworks may vary for healthcare providers practicing telehealth across state lines, posing logistical challenges for telehealth implementation.
Future Outlook: Despite these challenges, telehealth holds immense promise for the future of healthcare delivery in Connecticut. As technology continues to evolve and regulatory barriers are addressed, telehealth has the potential to become an integral part of the healthcare landscape, improving access to care, enhancing patient outcomes, and transforming the way healthcare is delivered and experienced in Connecticut and beyond.
Conclusion: Telehealth represents a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve access, convenience, and quality of care for individuals across Connecticut. By embracing telehealth solutions, healthcare providers, policymakers, and stakeholders can work together to overcome challenges, expand access to care, and create a more equitable and resilient healthcare system for all residents of Connecticut.